WIS 2.0 SRF products of WIPPS DC Moscow
Forecasting model: ICON-Ru13/6N29. Grid spacing: 0.25*0.25º. Start time: 00 and 12 UTC.
WIPPS DC Moscow Metadata at National Center MOSCOW node
WIPPS DC Moscow Metadata at DWD Global Discovery Catalogue
| Parameter | Level | Time step, hr | ||
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | ||
| Geopotential height, Temperature, Wind zonal and meridional velocity, Divergence, Vorticity |
925 hPa 850 hPa 700 hPa 500 hPa 250 hPa |
3 | 3 | 3 |
| Relative humidity | 925 hPa 850 hPa 700 hPa 500 hPa |
3 | 3 | 3 |
| Mean sea level pressure (MSLP) | Sea level | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Temperature, Dewpoint temperature, 3-hour minimum and maximum temperature |
Surface (2 m) | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Wind zonal and meridional velocity, Wind gust at 10 m |
Surface (10 m) | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Total precipitation, Convective precipitation, Precipitation type |
Surface | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| CAPE | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| Low and medium cloud coverage | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| Total cloud coverage | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
Limited-area short-range numerical weather prediction system description
Two systems for short-range limited area numerical weather prediction (NWP) are currently in use at the Hydrometcentre of Russia:
- System on the basis of ICON model (primary system since Autumn 2025);
- System on the basis of COSMO model (previous system).
Description of System on the basis of ICON model
1. System
- System name: ICON-Ru13/6N29
- Date of implementation: 01.12.2024
2. Configuration
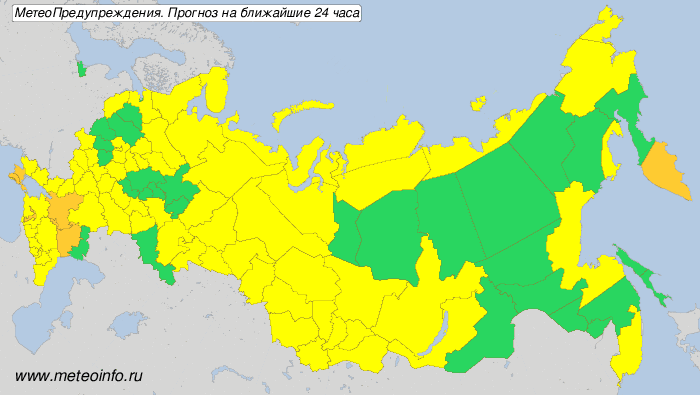
- Domain: Computational domain 29.5⁰-90⁰N, 180⁰W-180⁰E with grid spacing 6.5 km is nested into global domain with grid step 13km. Domain for forecast dissemination via WMO Information System 2.0 - to be identical to the COSMO-Ru6ENA subdomain (Fig.2, red contour)
- Horizontal resolution of the model, with indication of grid spacing in km: 6.5 km
- Number of model levels: 74
- Top of model: 23 km
- Forecast length and forecast step interval: 120 hr, 1 hr before 72 hr, 3 hr after 72 hr
- Runs per day: 4 (00, 06, 12, 18 UTC)
- Is model coupled to ocean, wave, sea-ice models? No
– Integration time step: 60 s
– Additional comments: nested to the global configuration (ICON-Ru13)
Fig.1. Subdomain of ICON-Ru13/6N29 system for forecast dissemination via WIS 2.0.
3. Initial conditions:
– Data assimilation method: None yet
– Additional comments: DWD (ICON) open data for the globe
4. Surface boundary conditions
– Sea-surface temperature? If yes, briefly describe method(s):
– Land-surface analysis? If yes, briefly describe method(s):
– Additional comments:
5. Lateral boundary conditions
– Model providing lateral boundary conditions: global configuration ICON-Ru13 (grid step of about 13 km)
– Lateral boundary conditions update frequency: two-way nesting, coupling with nested domain each 120 s
6. Other details of model
– What kind of soil scheme is in use? TERRA (with tile approach) (Heise, Schrodin, Shults)
– How are radiations parameterized? ecRad scheme, Aerosol climatology - CAMS climatology (Poliukhov A.A., Gvozdeva A.V., Piskunova D.A. - Effects of the Vertical Aerosol Structure on Short-range Air Temperature Forecasting and Clear-sky Shortwave Radiation Calculations in the ICON Model - Russian Meteorology and Hydrology, Allerton Press Inc. , Vol 49, № 8, pp. 711-721 DOI, Effects of aerosol climatologies on weather forecast in NWP models / A.A. Poliukhov, D. V. Blinov, N. Y. Chubarova et al. // AIP Conference Proceedings. — 2024, Vol. 2988, P. 080008. DOI: 10.1063/5.0182768)
– What kind of large-scale dynamics is in use (for example, grid-point semi-Lagrangian)? Grid-point Eulerian, triangular grid, Finite-volume method
- Hydrostatic or non-hydrostatic? Non-hydrostatic
– What kind of boundary layer parameterization is in use? Prognostic TKE
– What kind of convection parameterization is in use? Mass-flux shallow and deep convection
– What cloud/microphysics scheme is in use? Single-moment scheme, cloud diagnostic scheme by Koehler
– Other relevant details?
7. Further information
Operational contact point: Gdaliy Rivin (This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.)
URL for products charts: https://u2019.meteoinfo.ru/services/krasnoyarsk/workspace_1.php?type=map
More details about the ICON model - at https://www.icon-model.org/.
Description of the system on the basis of COSMO model
Numerical weather prediction system COSMO-Ru was implemented at the Hydrometcenter of Russia/Roshydromet in 2011 as a basic technology for short-range limited area weather forecasting. Since that time various components of the COSMO-Ru system have continiously evolved and modernized. In December 2024, after a parallel pre-operational trial it was decided to replace the operational system COSMO-RU by the new system ICON-RU. This transition was completed in autumn of 2025.
1. System
- System name: COSMO-Ru6ENA
- Date of implementation: 01.12.2020
2. Configuration
– Domain:
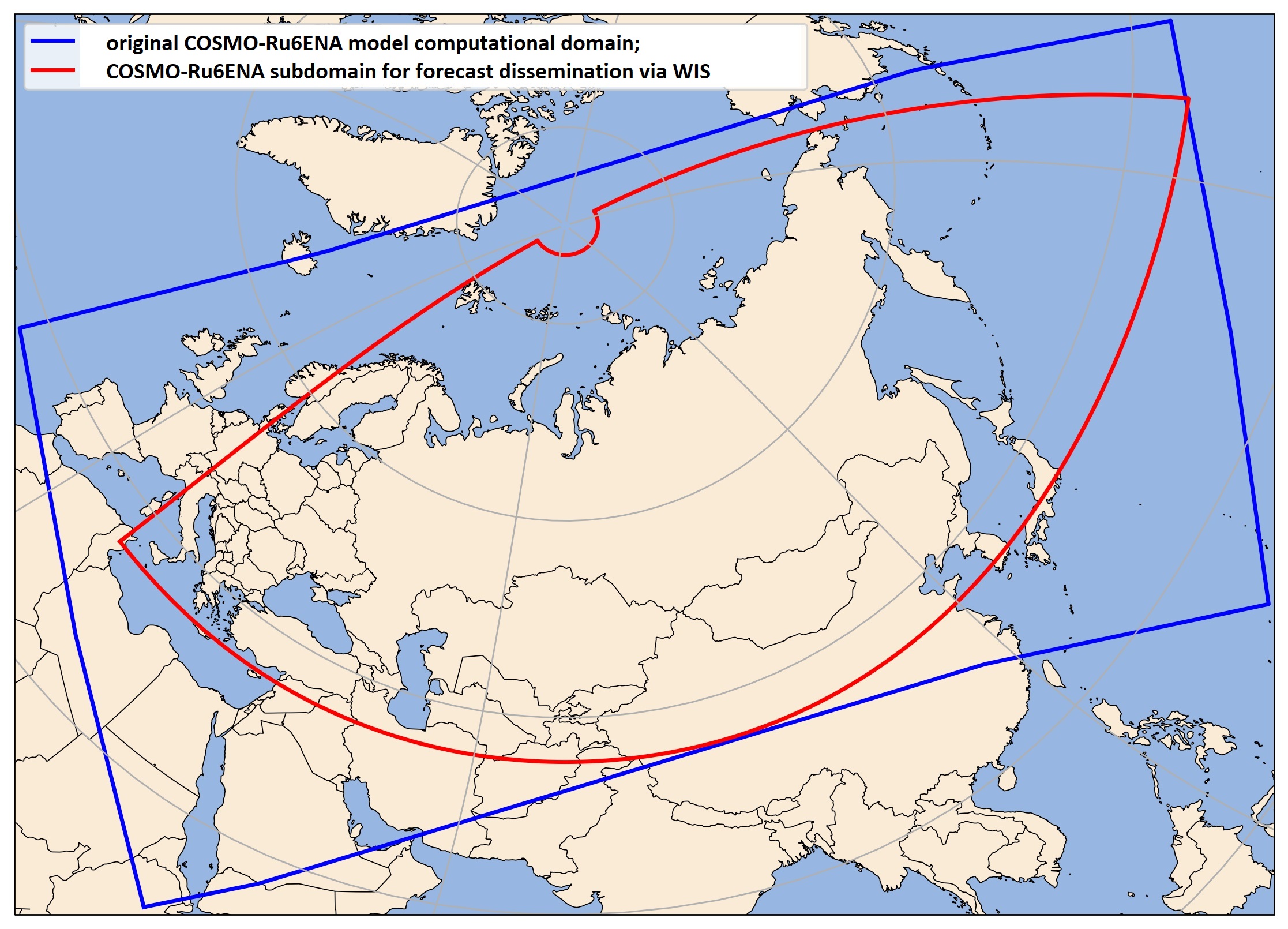
Fig.2. Computational domain of COSMO-Ru6ENA (blue contour) and its subdomain for forecast dissemination via the WMO Information System (red contour: 35°N-87°N, 19.5°E-193.5°E).
– Horizontal resolution of the model, with indication of grid spacing: 6.6 km (0.06° on rotated spherical latlon grid)
– Number of model levels: 40
– Top of model: 23 km
– Forecast length and forecast step interval: 120 h
– Runs per day (times in UTC): 4 (from 00, 06, 12, 18 UTC)
– Is model coupled to ocean, wave, sea-ice models? Specify which models: None
– Integration time step: 60 s
– Additional comments: None
3. Initial conditions
– Data assimilation method: Nudging
– Additional comments: Initial data are generated from initial data of ICON-Ru13/6N29 system (see below)
4. Surface boundary conditions
– Sea-surface temperature? If yes, briefly describe method(s): DWD (ICON) open data for the globe
– Land-surface analysis? If yes, briefly describe method(s): Nudging for near-surface atmospheric data, Cressman for soil temperature with using temperature at 2m from SYNOP data. Blinov D.V., Revokatova A.P., Rivin G.S. Assimilation of Observational Data in the COSMO-Ru Short-range Numerical Weather Prediction System of the Hydrometcenter of Russia //Russian Meteorology and Hydrology. – 2024, V. 49, №.7., P. 607-617. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068373924070057
– Additional comments: None
5. Lateral boundary conditions
– Model providing lateral boundary conditions: global component of ICON-Ru13/6N29 (grid step 13 km)
– Lateral boundary conditions update frequency: 3 h, one-way nesting
6. Other details of model
– What kind of soil scheme is in use? Multi-Layer soil and vegetation model TERRA_ML (Jacobsen and Heise); TERRA+FLAKE - upgraded TERRA (Mironov). More detais - https://www.cosmo-model.org/content/model/cosmo/coreDocumentation/cosmo_physics_6.00.pdf
– How are radiations parameterized? δ two-stream (Ritter-Geleyn). More detais - https://www.cosmo-model.org/content/model/cosmo/coreDocumentation/cosmo_physics_6.00.pdf
– What kind of large-scale dynamics is in use (for example, grid-point semi-Lagrangian)? Grid-point Eulerian (3rd order Runge-Kutta scheme, Arakawa-C/Lorenz staggered grid)
- Hydrostatic or non-hydrostatic? Non-hydrostatic, full compressible hydro-thermodynamical equations in advection form
– What kind of boundary layer parameterization is in use? Prognostic TKE-Based Surface Transfer Scheme. More detais - https://www.cosmo-model.org/content/model/cosmo/coreDocumentation/cosmo_physics_6.00.pdf
– What kind of convection parameterization is in use? Max-flux (Tiedtke-Bechold, 2014) for shallow, penetrative and midlevel convection. More detais - https://www.cosmo-model.org/content/model/cosmo/coreDocumentation/cosmo_physics_6.00.pdf
– What cloud/microphysics scheme is in use? Seifert-Beheng Two-moment cloud microphysical scheme
– Other relevant details?
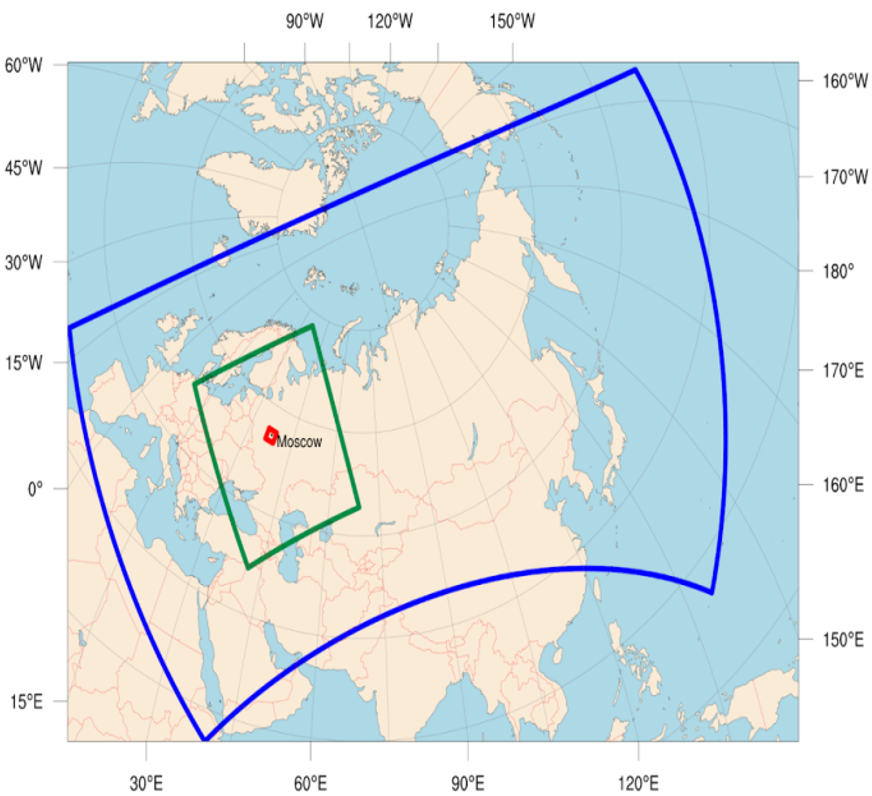
Fig.3. Hierarchy of COSMO-Ru computational domains: Blue contour - 6.6 km grid spacing, green contour - 2.2 km, red - 1 km.
Rapid update cycle with nudging assimilation of radar precipitation data is implemented for the nested domain with 2.2 km grid spacing.
7. Further information
Operational contact points: Gdaliy Rivin email: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it., Inna Rozinkina email This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
URL for products charts: https://meteoinfo.ru/en/cosmo-ru6-maps, https://u2019.meteoinfo.ru/services/krasnoyarsk/workspace_1.php?type=map
URL for system documentation: description of technology and testing results: https://method.meteorf.ru/publ/sb/sb49/02.pdf (in Russian)
Links to the documentation of the latest version 6.0 of the COSMO model, containing a description of all its blocks (dynamic, physical and data assimilation) are available at https://www.cosmo-model.org/content/model/cosmo/default.htm.
Products for WMO information system
Forecasting model: COSMO-RU. Grid spacing: 0.5*0.5º. Start time: 00 and 12 UTC.
Subseasonal forecasts
Global deterministic and ensemble medium-range forecasting system description
- System
– System name (version): SL-AV10
– Date of implementation: 17.10.2023
- Configuration
– Horizontal resolution of the model, with indication of grid spacing in km: 0.1° in longitude, variable resolution in latitude from 0.13° (11-15 km) in the extratropical part of Southern hemisphere to 0.08° (8-13 km) in midlatitudes of the Northern hemisphere.
– Number of model levels: 104
– Top of model: 0.04 hPa
– Forecast length and forecast step interval:
For 00 UTC, forecast fields are available from 3 to 120 hours with the step of 3 hours (some fields with the step of 6 hours ).
For 12 UTC, forecast fields are available from 3 to 240 hours. Up to 120 hours temporal resolution is 3 hours (for some fields 6 hours); for lead times 132-168 hrs forecast fields are written every 12 hours; for lead times 192-240 hrs forecast fields are written every 24 hours.
– Runs per day: 2, from 00 and 12 UTC
– Is model coupled to ocean, wave, sea-ice models? Specify which models: No
– Integration time step: 270 s
– Additional comments: None
- Initial conditions
– Data assimilation method: 3D-Var
– Additional comments: None
- Surface boundary conditions
– Sea-surface temperature? If yes, briefly describe method(s): OSTIA data
– Land-surface analysis? If yes, briefly describe method(s): ISBA assimilation scheme ( Giard D., Bazile E. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2000, 997-1015) as implemented in (Bogoslovskii et al, J. Comput. Technologies, 2008)
– Additional comments: None
- Other details of model
– What kind of soil scheme is in use?: ISBA (Noilhan J., Mahfouf J.-F. Global Planet Change. 1996, p. 145-149).
– How are radiations parameterized?: CLIRAD SW (Tarasova T.A., Fomin B.A. Atm. Ocean. Technol. 2007. p. 1157-1162), RRTMG LW (Mlawer E.J., Taubman S.J., Brown P. D., Iacono M.J., Clough S.A. J. Geoph. Res.: Atmos. 1997. p. 16663-16682)
– What kind of large-scale dynamics is in use (for example, grid-point semi-Lagrangian)?: Grid-point semi-Lagrangian (Tolstykh et al, Geosci. Mod. Devel. 2017, 1961-1983), hybrid vertical coordinate
Hydrostatic or non-hydrostatic?: Hydrostatic
– What kind of boundary layer parameterization is in use?: TOUCANS (Durán I.B., Geleyn J.-F., Vána F. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014), (Durán I.B., Geleyn J.-F., Vána F. J., Schmidli J., Brozkova R. Atmos. Sci. 2018)
– What kind of convection parameterization is in use?: Modified Bougeault scheme (Gerard L., Geleyn J.-F., Quart J.Roy.Met.Soc. 2005) with modifications by R. Fadeev (Fadeev 2023, Tolstykh et al 2024)
– What cloud scheme is in use?: Xu-Randall (Gerard L., Piriou J.-M., Brozkova R., Geleyn J.-F., Banciu D. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2009), subinversion clouds by R. Fadeev (2018).
– Other relevant details?: None
- Further information
– Operational contact point: Mikhail Tolstykh email: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
– URLs for system documentation: https://elibrary.ru/download/elibrary_35574057_38171365.pdf
– URL for list of products: https://meteoinfo.ru/en/wmc-moscow-products
Ensemble system description
- Ensemble system
– Ensemble name (version): EnSL-AV
– Date of implementation: 01/08/2022
- Configuration of the Ensemble Prediction System
– Horizontal resolution of the model, with indication of grid spacing in km: 0.72x0.9° lat-lon (approximately 75 km)
– Number of model levels: 96
– Top of model: 0.04hPa
– Forecast length and forecast step interval: 10 days, step - 12 hours
– Runs per day (times in UTC): one (00UTC)
– Is there an unperturbed control forecast included? yes
– Number of perturbed ensemble members (excluding control): 40
– Is model coupled to ocean, wave, sea‑ice models? Specify which models: No
– Integration time step: 1200s
– Additional comments:
- Initial conditions and perturbations
– Initial perturbation strategy: LETKF assimilation with multiplicative and additive inflation; analyses are then centered to operational 3D Var analysis.
– Optimization time in forecast (if applicable): N/A
– Horizontal resolution of perturbations (if different from model resolution):
– Initial perturbed area: Global
– Data assimilation method for control analysis: 3D Var
– Are perturbations to observations employed? If so, which observation types are perturbed? No
– Perturbations added to control analysis or derived directly from ensemble analysis: Perturbations are derived directly from ensemble analysis
– Perturbations in +/‑ pairs? No
– Additional comments: None
- Model uncertainty perturbations
– Is model physics perturbed? If so, briefly describe method(s): SPP + SPPT for temperature and vorticity equations.
– Do all ensemble members use exactly the same model version, or are, for example, different parameterization schemes used? Please describe any differences: The same model version is used
– Is model dynamics perturbed? If so, briefly describe method(s): No
– Are the above model uncertainty perturbations applied to the control forecast? No
– Additional comments: None
- Surface boundary perturbations
– Perturbations to SST? If so, briefly describe method(s): No
– Perturbations to soil moisture? If so, briefly describe method(s): T2m and RH2m analyses used for soil moisture correction are produced for each ensemble member with respective background fields.
– Perturbations to surface wind stress or roughness? If so, briefly describe method(s): None
– Any other surface perturbations? If so, briefly describe method(s): None
– Are the above surface perturbations applied to the control forecast? None
– Additional comments: None
- Other details of model
– What kind of soil scheme is in use? ISBA
– How are radiations parameterized? CLIRAD SW (Tarasova, Fomin 2005) + RRTMG LW (Mlawer et al 1997)
– What kind of large‑scale dynamics is in use (for example, grid‑point semi‑Lagrangian)? Grid-point semi-Lagrangian, absolute vorticity equation is solved. (Tolstykh et al GMD 2017)
Hydrostatic or non‑hydrostatic? Hydrostatic
– What kind of boundary layer parameterization is in use? Bastak-Duran et al (JAS 2014)
– What kind of convection parameterization is in use? Bougeault (MWR 85), Ducrocq and Bougeault (95), Gerard and Geleyn (QJ 2005) with our modification of momentum transport
– What cloud scheme is in use? Xu-Randall (JAS 96), diagnostic
– Other relevant details?
- Products
– Method of the calculation, if the method is not unique:
– Other detailed specifications, if necessary:
- Further information
– Operational contact point: Vassily Mizyak This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
– URLs for system documentation:
– URL for list of products: